
StateFlow vs SharedFlow
StateFlow
- StateFlow는 현재 상태와 새로운 상태 업데이트를 내보내는 Observable 상태 홀더 flow이다.
- value 속성을 통해서 현재 상태 값을 읽을 수 있으며 상태를 업데이트 하고 전송하려면 MutableStateFlow 클래스의 value 속성에 새 값을 할당한다.
- 값이 업데이트 된 경우에만 반환하고 동일한 값은 반환하지 않는다.
- Flow는 일반적으로 Cold Stream 이지만, StateFlow는 Hot stream이다.
- 식별 가능한 변경 가능 상태를 유지해야 하는 클래스에 적합하다.
Sunflower 프로젝트 내 Stateflow 예시)
@HiltViewModel
class PlantListViewModel @Inject internal constructor(
plantRepository: PlantRepository,
private val savedStateHandle: SavedStateHandle
) : ViewModel() {
private val growZone: MutableStateFlow<Int> = MutableStateFlow(
savedStateHandle.get(GROW_ZONE_SAVED_STATE_KEY) ?: NO_GROW_ZONE
)
val plants: LiveData<List<Plant>> = growZone.flatMapLatest { zone ->
if (zone == NO_GROW_ZONE) {
plantRepository.getPlants()
} else {
plantRepository.getPlantsWithGrowZoneNumber(zone)
}
}.asLiveData()growZone은 StateFlow로 내부 값에 따라서 GROW_ZONE_SAVED_STATE_KEY or NO_GROW_ZONE
으로 결정되며 마지막에 들어온 값에 따라 LiveData인 plants값이 변한다.
예제코드
fun main() = runBlocking<Unit> {
val stateFlow = MutableStateFlow<Int>(99)
launch {
var x = 1
stateFlow.value = x
repeat(20) {
stateFlow.emit(x++)
delay(100L)
}
}
launch {
delay(500L)
stateFlow.collect {
println("$it 수집")
}
}
}
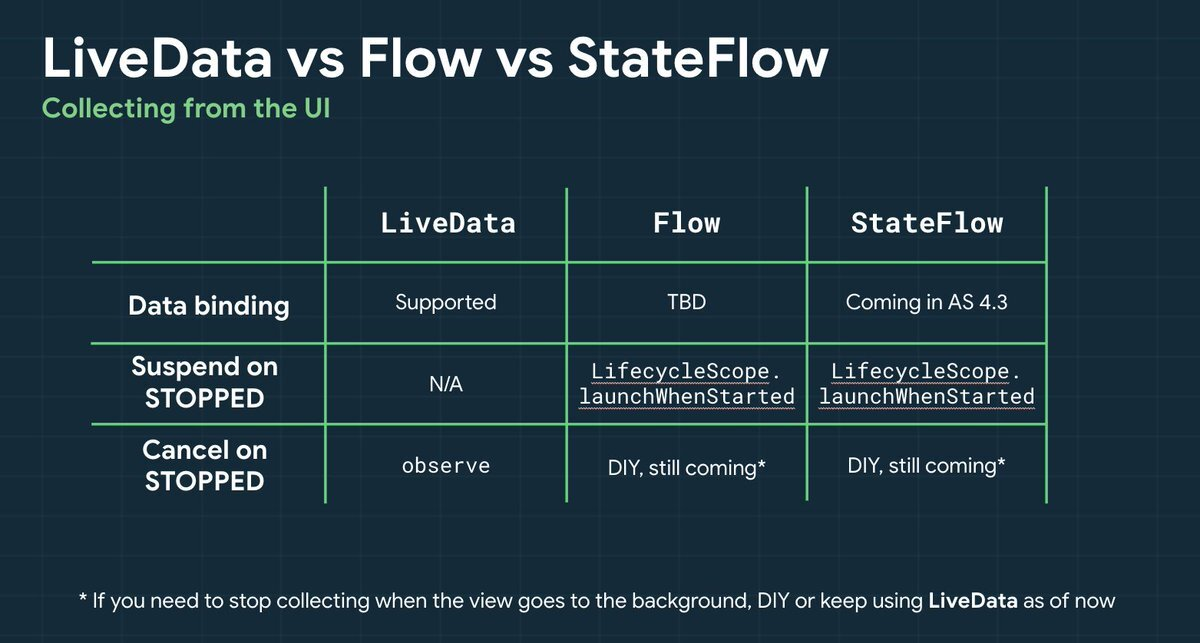
StateFlow, Flow, LiveData
StateFlow 와 LiveData는 비슷한 점이 많다. 둘 다 관찰 가능한 데이터 홀더 클래스이며, 앱 아키텍처에 사용할 때 비슷한 패턴을 따릅니다.
Flow builder로 생성한 flow들은 기본적으로 Cold stream 이다. 하지만 Stateflow & Sharedflow 는 Hot stream 이다.
Cold stream
- collect() (또는 이를 subscribe 할 때)를 호출할 때 마다 flow block이 재실행 된다. 즉 1~10까지 emit 하는 flow가 있다면 collect 할 때 마다 1~10을 전달 받는다. 여러 곳에서 collect를 호출하면 각각의 collect에서 1~10을 전달받는다.
Hot stream
- collect (또는 이를 subscribe 할 때)를 호출하더라도 flow block이 호출되지 않는다. collect() 시점 이후에 emit 된 데이터를 전달받는다.
StateFlow vs LiveData
- StateFlow - 초기값 O ↔ LiveData - 초기값 X
- View가 Stopped 상태가 되면 LiveData.observe() 는 자동으로 관찰을 취소하지만, StateFlow 는 다른 Flow에서 수집하는 경우 자동으로 중지하지 않는다. 동일한 동작을 실행하려면 LifeCycle.repeatOnLifecycle 블록에서 flow를 collect() 해야한다.
Stateflow lifecycle 처리
class LatestNewsActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
private val latestNewsViewModel = // getViewModel()
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
...
// Start a coroutine in the lifecycle scope
lifecycleScope.launch {
// repeatOnLifecycle launches the block in a new coroutine every time the
// lifecycle is in the STARTED state (or above) and cancels it when it's STOPPED.
repeatOnLifecycle(Lifecycle.State.STARTED) {
// Trigger the flow and start listening for values.
// Note that this happens when lifecycle is STARTED and stops
// collecting when the lifecycle is STOPPED
latestNewsViewModel.uiState.collect { uiState ->
// New value received
when (uiState) {
is LatestNewsUiState.Success -> showFavoriteNews(uiState.news)
is LatestNewsUiState.Error -> showError(uiState.exception)
}
}
}
}
}
}
SharedFlow
- SharedFlow를 사용하면 모든 콘텐츠가 주기적으로 동시에 새로고침되도록 앱의 나머지 부분에 전송할 수 있습니다. ex) 최신 뉴스 가져오기, 주제 컬렉션으로 사용자 정보 섹션 새로고침..
- StateFlow는 기본적으로 새 구독자가 있을 때 마지막으로 알려진 값을 내보낸다. SharedFlow를 사용하면 내보낼 collect() 이전 값 수 를 구성할 수 있다.
- 값의 버퍼가 가득 찼을 때 동작을 정의할 수 있다.
Google Developer Sharedflow 예시)
// Class that centralizes when the content of the app needs to be refreshed
class TickHandler(
private val externalScope: CoroutineScope,
private val tickIntervalMs: Long = 5000
) {
// Backing property to avoid flow emissions from other classes
private val _tickFlow = MutableSharedFlow<Int>(
replay = 0,
extraBufferCapacity = 1,
onBufferOverflow = BufferOverflow.DROP_OLDEST
)
val tickFlow: SharedFlow<Event<String>> = _tickFlow
init {
externalScope.launch {
while(true) {
_tickFlow.emit(Unit)
delay(tickIntervalMs)
}
}
}
}
class NewsRepository(
...,
private val tickHandler: TickHandler,
private val externalScope: CoroutineScope
) {
init {
externalScope.launch {
// Listen for tick updates
tickHandler.tickFlow.collect {
refreshLatestNews()
}
}
}
suspend fun refreshLatestNews() { ... }
...
}
예제코드
fun main() = runBlocking<Unit> {
val sharedFlow = MutableSharedFlow<Int>(
replay = 2,
extraBufferCapacity = 1,
onBufferOverflow = BufferOverflow.DROP_OLDEST
)
launch {
var x = 1
repeat(20) {
sharedFlow.emit(x++)
delay(100L)
}
}
launch {
delay(500L)
sharedFlow.collect {
println("$it 수집")
}
}
}
replay
collect시 전달받을 이전 데이터의 개수를 지정합니다. replay가 0이라면 collect 시점에 담겨있던 데이터부터 전달받을 수 있습니다. 만약 1이라면 collect 시점 직전의 데이터부터 전달받으며 시작합니다. 만약 2라면 현재 데이터 이전 두개의 데이터 부터 전달받으면서 시작하게 됩니다.
예를 들어 0~9까지 emit 되는 state flow에서 3이 emit 되어 시점에 collect가 시작된다면
ex) 0->1->2->3-> collect 시작->4->5->6->7->8->9
- replay = 0 일 때: 4부터 수신 시작
- replay = 1 일때: 3부터 수신 시작
- replay = 4 이상 일때: 0부터 수신 시작
extraBufferCapacity
buffer 개수 설정을 설정합니다. flow의 emit이 빠르고 collect가 느릴 때 지정된 개수만큼 buffer에 저장되면 저장된 개수가 넘어가면 onBufferOverflow에 설정된 정책에 따라 동작하게 됩니다.
onBufferOverflow
Buffer가 다 찼을 때의 동작을 정의합니다. 이는 channel에서 사용하는 buffer의 정의와 동일합니다.
- BufferOverflow.SUSPEND : buffer가 꽉 찼을 때 emit을 수행하면 emit 코드가 blocking 됩니다. 즉, buffer의 빈자리가 생겨야 emit 코드 이후의 코드가 수행될 수 있습니다.
- BufferOverflow.DROP_OLDEST: buffer가 꽉 찼을 때 emit을 수행하면 오래된 데이터 부터 삭제하면서 새로운 데이터를 넣습니다.
- BufferOverflow.DROP_LATEST: buffer가 꽉찼을때 emit을 수행하면 최근 데이터를 삭제하고 새로운 데이터를 넣습니다.
출처 : https://tourspace.tistory.com/434
참고